Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
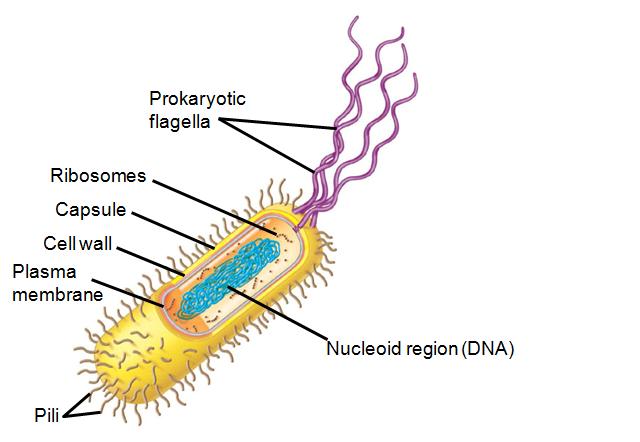
Prokaryotic cells have a small, simple structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They also have less surface area per volume. Prokaryotes do not have a true nucleus: the DNA is in the nucleoid region rather than a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells have only: prokaryotic flagella, pili, capsule, cell wall, plasma membrane, ribosomes, and nucleoid region with DNA. Together, the pili, capsule, cell wall, and plasma membrane are called a cell envelope. Eukaryotic cells do not have a cell envelope, as both animal and plant cells lack pili and a capsule and plant cells do not have a cell wall.
Prokaryotic cells lack most organelles, for example a mitochondrion, chloroplasts, and cilia. They reproduce through binary fission. Some examples of prokaryotes are bacteria and archae.
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal Cell

Plant Cell

Eukaryotic cells have a large, complex structure compared to prokaryotic cells. They also have more surface area per volume. Eukaryotes have a true nucleus: the DNA is in a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have: nucleolus, nucleus, rough ER, smooth ER, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, mitochondrion, peroxisome, and plasma membrane. The cytoskeleton comprises (in order from smallest to largest) microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Only animal cells have flagella, lysosomes, and a centriole. Only plant cells have chloroplasts, a cell wall, and a central vacuole. Eukaryotic cells reproduce through mitosis and meiosis. Some examples of eukaryotes are plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Eukaryotic cells are highly compartmentalized. That means membranes and membrane systems within the cell separate materials (ex. glucose, water, oxygen, poisons) from the rest of the cell and separate organelles from each other. Within the membranes, different parts of the cell do their individual jobs.
All cells can only grow to a certain size. They need surface area to carry out reactions, and if they are too large, there is not enough surface area per volume.
The rough ER and smooth ER are found in animal and plant cells, but not prokaryotes.
"A Tour of the Cell." PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition. Campbell, Reese, Taylor, and Simon; lectures by Chris Romero. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings.
Ducks Deluxe
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Project
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.